Sterile Processing
How to Use Ultrasonic Indicators in Medical Device Processing
In healthcare, ensuring that surgical instruments are thoroughly cleaned before sterilization is not just best practice; it’s a critical safeguard for patient safety. If a device is not cleaned properly, it can’t be sterilized properly. As surgical procedures become more complex and... Read MoreMaximizing your Robotic Surgery Investment
More than 9,500 da Vinci® surgical systems are installed worldwide1, and over 10 million robotic-assisted surgical procedures are performed every year.2 Robotic-assisted surgery (RAS) isn't the future; it is a dominant technology today... Read MoreHow to Load Washer Racks in Sterile Processing
Efficient washer rack loading helps ensure that medical instruments are thoroughly cleaned and ready for the next step in reprocessing. Improper rack loading can lead to instruments not being cleaned properly, re-work, and washer loads needing to be run through the cycle again... Read MoreOptimizing Sterile Processing Operations
To optimize sterile processing department (SPD) operations, the department needs the resources to be successful and the capability to manage people, processes, and technology effectively. Understanding what resources are needed, referred to as Organizational Capacity and Operational Performance, as well as how to manage the department effectively, are the first steps to improving... Read MoreEndoscope Manual Cleaning & Point-of-Use Treatment Guide
Manual cleaning is arguably the most important step when processing an endoscope. If residual soils or bioburden remain on the device, high-level disinfection (HLD) or liquid chemical sterilization (LCS) may not be achieved. Blood, complex carbohydrates, and proteins could flow into small lumens, grooves, or other difficult-to-clean locations... Read MoreExpanding Sterilization Options for Medical Devices
Sterilization renders a medical device free from viable microorganisms to help prevent the transmission of harmful organisms to patients and help reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections (HAI). According to the United States Food & Drug Association (FDA)... Read MoreManaging a Water Crisis in Sterile Processing
Sterile processing professionals are tasked with managing hundreds of instruments daily, staff shortages, and so much more. Policies and procedures are often in place for common occurrences, such as a failed quality test, but one thing a department manager may not be prepared for... Read MoreSPD Staffing & Training: Critical To An Effective Sterile Processing Program
Effective sterilization of surgical instruments and devices is critical. The Sterile Processing Department (SPD) technicians' primary role is to clean, sterilize, store, and track surgical instruments and devices used in medical procedures. Improperly processed surgical instruments can impact patients' safety... Read MoreWhat is Offsite Reprocessing
The Sterile Processing Department (SPD) is a highly critical department at a healthcare facility. The SPD is responsible for cleaning, decontaminating, sterilizing, and preparing surgical instruments for the Operating Room (OR). Many SPDs face challenges daily, from influxes in surgical case volumes and staffing shortages... Read MoreCapital Budgeting in Sterile Processing
Gaining approval for capital improvement projects in hospital sterile processing departments (SPD) can be challenging. It is important for Department Managers to focus on highlighting the benefits this capital investment will have... Read MoreImportance of Leak Tests in Steam Sterilization
Medical steam sterilizers, or autoclaves, remove air from a chamber and replace it with moist heat steam for a certain amount of time, inactivating and destroying microorganisms at a cellular level...1 Read MoreBowie-Dick Tests and Troubleshooting Guide
Bowie-Dick (Air-Removal) tests evaluate the performance of prevacuum sterilizers by confirming adequate air removal from the sterilizer chamber. These air removal tests have been improved over the years, but you may be wondering...
Read MoreEndoscope Drying and Storage Cabinet Guidelines
Endoscopes are complex instruments with long, narrow channels that can be difficult to clean and prepare for next procedure. Helping prevent patient infections requires endoscope reprocessing after each use, following a process outlined by the device's instructions for use... Read MoreGuide to Reprocessing Robotic Surgery Instruments
Robotic surgery, also called robot-assisted surgery (RAS), is performed using small devices attached to a larger robotic arm. These delicate and complex surgical instruments allow for smaller incisions, better vision, and... Read MoreGuide to Sterilization of Flexible Endoscopes in Healthcare
Flexible endoscopes in healthcare are used in various medical procedures to diagnose and treat conditions such as reflux, ulcers, polyps, and other intestinal diseases... Read MoreGuide to Ultrasonic Cleaning of Medical Devices: How Ultrasonics Work and More
Ultrasonic cleaners in hospitals provide an automated cleaning process for surgical instruments and support compliance with the manufacturer's instructions for use (IFUs) of those instruments. Many complex instruments have... Read MoreWater Quality Medical Device Processing
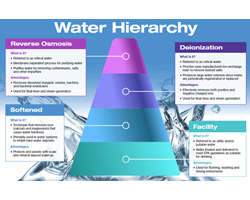
Water is used to clean, disinfect, and sterilize millions of medical devices daily. Tap water isn't sufficient for all device processing steps. Quality water for processing instruments improves cleaning chemistry effectiveness, reduces corrosion/damage, and improves steam quality for sterilization... Read MoreRapid-Read Biological Indicators
Rapid-read biological indicators (BIs) can improve productivity in the Sterile Processing Department (SPD) by keeping the process moving - especially when departments implement standardization and monitor every load. By enabling the release of the loads faster, a 20-minute rapid-read BI... Read MoreWhat is a Medical Washer Disinfector?
A Medical Washer/Disinfector are a medical device used for automated cleaning of surgical instruments and work by combining impingement, water temperature, and detergent to clean heat-resistant and heat-sensitive devices... Read MoreWhat is Endoscope Reprocessing?
Endoscope processing is the process of cleaning and disinfecting reusable endoscopes before patient use. Due to the complex, intricate design, flexible and semi-rigid endoscopes should be handled properly to prevent damage, and device instructions for use (IFU) should be followed or proper reprocessing... Read MoreComparing Options for Rapid Turn / Immediate Use Sterilization
Surgical procedures do not always go as planned. An instrument arrives in the operating room (OR) with a tear in the sterile packaging, or a unique instrument is dropped, and the procedure cannot continue without it. Mistakes happen, and undeniably there are instances where a device needs to be reprocessed faster than normal… Read MoreHidden Cost of your Aging Washer
Your current "old faithful" washer/disinfector in sterile processing has worked great for years, but is it costing you more and more each year... Read MoreNew Technologies in Steam Sterilization
It is no secret that steam sterilizers are the reliable work horse of the sterile processing department (SPD). With growing caseload volumes facing many facilities it is important to consider the advantages modern steam sterilizers provide your department to help it run at peak efficiency... Read MoreEndoscopy Reprocessing Standards are Evolving
Endoscopy procedures are some of the fastest-growing medical procedures in the world. More than 250 million endoscopies are performed each year globally, with this number continuing to grow year over year1. With that, standards and regulations are constantly evolving... Read MoreGuide to High-Level Disinfection of Endoscopy Devices
High-level disinfection, also known as HLD, is the complete elimination of all microorganisms in or on an instrument, except for small numbers of bacterial spores.1 The FDA further defines a high-level disinfectant as a sterilant used for... Read MoreGuide to Optimal Steam Generation
All types of steam can provide effective sterilization, but healthcare facilities have choices and should understand the different types of steam generation available. Everyone wants to minimize the occurrence of wet packs, instrument staining, chamber scale/rouge, rouge and other associated challenges, but all of these which depend upon your the quality of... Read MoreSelecting the Right Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic cleaning systems provide an automated solution for delicate or highly intricate medical devices. To perform ultrasonic cleaning, an ultrasonic washer uses a cleaning solution, cavitation, and.... Read MoreAchieve 510(k) Clearance for Automated Cleaning Process for Select da Vinci Instruments
In 2018, FDA provided guidance around reprocessing instructions for reusable medical devices, which includes robotic surgical instruments. This FDA guidance outlined requirements for manufacturers... Read MoreKey Considerations When Selecting a Washer Disinfector
There are several considerations when planning for a washer/disinfector purchase, and it begins with reviewing the devices that need to be processed in that washer/disinfector. What is your current instrument and rigid container inventory? How often does it need to be reprocessed... Read MoreWhat is a Chemical Indicator?
Chemical Indicators (CIs), as defined by AAMI and ISO, are devices used to monitor the presence or attainment of one or more of the parameters required for a satisfactory sterilization process or used in a specific test of sterilization equipment. For example, when placed inside packs, CIs are used to confirm that sterilant achieved good penetration in the items being sterilized. CIs are used as...
Read More
V-PRO beats STERRAD™ with a
1-2 Punch
In a head-to-head comparison of V-PRO vs. STERRAD™, it's clear that V-PRO beats STERRAD™ with a one-two punch in both throughput and material compatibility. This winning combination allows...
Read More
Container Processing at Ambulatory Surgery Centers
Ambulatory surgery center (ASC) caseloads are growing 6% to 7% each year1 with orthopedic, cardio, and spine procedures growing the fastest. Combine that with ASC procedure costs that are 35% to 50% lower than at a hospital2, the future becomes clear: ASCs will likely become a more popular choice for many...
Read MoreToday's SPD Guide to Washing and Decontamination Medical Equipment
Sterilization of medical devices started with the goal of reducing infections. Surgeons were often responsible for the cleaning and sterilization of their own surgical instruments and instruments were sterilized in the Operating Theater. In 1928, the American College of Surgeons realized that this was not the safest... Read MoreBenefits of Instrument Tracking Software
Instrument tracking software has evolved over time, from early basic applications letting Technicians identify the sterile status of a set and its location, to the newer, more sophisticated programs that help Sterile Processing Department (SPD) professionals manage different aspects of their instrument processing workflow. With increased caseloads... Read MoreHow to Track Loaner Surgical Instrument Trays
Loaner surgical instruments are unavoidable and offer healthcare facilities access to a wider variety of instruments and surgical devices. Loaner trays are often needed for specialized procedures... Read MoreGuide to Sterilization Pouches in Sterile Processing
A sterilization pouch, also known as a peel pack, is a disposable package specifically designed to be used in a sterilizer to allow penetration of the sterilant to the items placed inside. After sterilization, these Class II Medical Devices maintain sterility of the processed item. Sterilization pouches require... Read MoreImprove Steam Sterilizer Load Drying: Stop Cracking the Sterilizer Door
Cracking the door at the end of a steam sterilization cycle goes back to the days of gravity-only sterilization cycles when woven cotton muslin wraps with good absorption properties were commonly used to wrap instrument sets. With the reduced likelihood of external water... Read MoreHealthcare Sustainability
Sterile Processing Departments (SPDs) play a critical role in positive patient outcomes and staff safety. Each day, sterile processing professionals are tasked with safely and efficiently processing surgical instruments and medical devices. But how sustainable is the sterile processing... Read MoreSurgical Instrument Cleaning Chemistries
Cleaning, which refers to the removal of soil from a medical device or instrument, is a critical step when processing instruments in the sterile processing department (SPD). As the name implies, instrument cleaning chemistries are solutions specifically formulated to aid in the removal of organic and inorganic soils from medical instruments and other devices used during patient procedures... Read MoreGuide to Gravity IUSS Cycle Monitoring
Routine monitoring of steam sterilizers with biological indicators (BIs) applies to all types of cycles performed in autoclaves – including immediate use steam sterilization (IUSS) cycles. Previously referred to as "flash sterilization," these... Read MoreGuide to Stainless Steel Corrosion Removal
Sterile Processing Departments (SPDs) inevitably must deal with stainless steel corrosion, also called rouge. Corrosion on steam sterilizers is caused by a chemical reaction between moisture and stainless steel. While corrosion is often an issue many know little about, it is important to... Read MoreInstrument Cleaning Brushes
Using the right tool for the job is important and one of the keys to effective cleaning is having the right instrument cleaning brush. This article will review how to choose the correct...Read More
What is Sterility Assurance Monitoring?
Sterility assurance monitoring is a vital component of your overall quality assurance protocol. Sterility assurance products such as Biological Indicators (BI) and Chemical Indicators (CI) give you the confidence that the sterilizer in use is functioning properly and cycle conditions are adequate to produce medical devices and... Read More4 Steps to Make the Switch to V-PRO
You’ve made the decision to change from one low temperature sterilizer to another after considering multiple factors and finding the ideal solution for your Sterile Processing Department (SPD)... Read MoreLiquid Chemical Sterilization
Liquid Chemical Sterilization (LCS) is used to sterilize heat-sensitive, immersible medical devices. When a device is liquid chemically sterilized, it is completely immersed in a sterilant solution for a prescribed period of time at a controlled temperature and concentration of active solution. Validation of efficacy requires demonstration of... Read MoreWhat if One Chemical Indicator Fails?
Everything was done as expected – the devices went through decontamination, completed a successful washer and thermal disinfection cycle, and were inspected, prepared and packaged successfully following all steps outlined in the instrument tracking software... Read MoreGuide to VHP Low Temperature Sterilization
Tasks performed prior to sterilization influence the success of any sterilization process. Key steps taken during decontamination, preparation and packaging... Read MoreThe Role of Chemical Indicators in Load Release
Chemical indicators (or CIs) are a necessary part of any healthcare facility's sterility assurance program. Since the introduction of the Bowie and Dick Test in 1969, the use of chemical indicators has expanded to cover a wide range of sterilization and high-level disinfection monitoring applications... Read MoreHow to Monitor Extended Steam Sterilization Cycles
Extended cycles are specific to steam sterilization where the exposure or dry times of a standard sterilizer cycle (i.e. 270°F for 4 minutes) have been adjusted. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) defines extended cycles as “any sterilization cycle that includes specifications that deviate from... Read MoreHow to Evaluate VHP Sterilizers for Your Facility
When considering options for vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP) sterilizers, it's important to understand the differences between available systems... Read MoreBiological Indicators
What are Biological Indicators?
Biological indicators (BIs), as defined by ANSI/AAMI and ISO, are test systems containing viable microorganisms providing a defined resistance to a specific sterilization process. A biological indicator provides information on whether necessary conditions were met to kill...
Read MorePositive BI Troubleshooting Checklist
Wondering what to do after a failed biological indicator test? Learn what to do after a positive BI and steps to follow to troubleshoot any issues in this STERIS Knowledge Center article. Read MoreThe Cost of Not Monitoring Every Load
Learn why one facility switched to every load monitoring in both STEAM and VHP sterilizers. Discover how load recalls impact the Sterile Processing Department as well as operating rooms costs associated with any downtime. Read MoreEverything About Autoclaves
What is an autoclave?
Autoclaves are also known as steam sterilizers, and are typically used for healthcare or industrial applications. An autoclave is a machine that uses steam under pressure to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores on items that are placed inside a pressure vessel. The items are heated to an appropriate sterilization temperature for a given amount of time. The moisture in the steam efficiently transfers heat...
Read MoreGuide to Steam Sterilization Cycles - Steam Flush Pressure Pulse
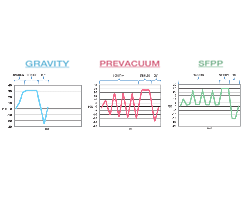
There are three types of steam sterilization cycles recognized by the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI). They are gravity, prevacuum and steam flush pressure pulse (SFPP). These cycles differ in the way air is removed from the load during conditioning and may have different exposure times depending on the type of...
Read MoreHydrogen Peroxide Sterilization
What is Hydrogen Peroxide Sterilization?
Hydrogen peroxide sterilization is a low temperature sterilization process commonly used in the application of sterilizing medical devices, often used to sterilize heat-sensitive devices. A hydrogen peroxide sterilization cycle typically requires less time than alternative forms of sterilization, such as steam sterilization. A hydrogen peroxide sterilization process involves...
Read MoreSteam Sterilization for Medical Equipment
Benefits of Steam Sterilization
Steam sterilization has many benefits as a sterilization method in healthcare facilities including low cost, safety, and efficacy. When processing heat and moisture stable materials...
Read MoreWhat is Sterile Processing
sterile processing department
The Sterile Processing Department (SPD), also known as the Central Sterile Services Department (CSSD), is the area in a hospital where cleaning and sterilization of devices used in medical procedures takes place. The processes an instrument goes through....
Read MoreWhat is an Enzymatic Cleaner
An enzymatic cleaner is used in healthcare facilities to aid in the cleaning and decontamination of medical devices and other medical equipment and utensils. Enzymatic cleaners used in the Endoscopy and Sterile Processing Departments may be better known as enzymatic detergents, because they contain surfactants designed to...
Read More





















.png?h=200&iar=0&w=250&hash=503980E0268C5010A14277974927F19E)