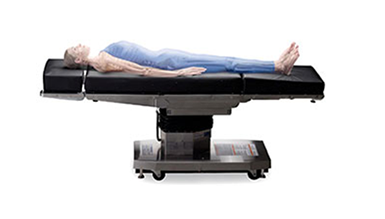
Surgical Table Pads
STERIS general surgical tables and specialty tables are supplied with premium pressure management pads for patient comfort and a significant measure of prevention against decubitus ulcers. The tabletop pads are available in different thicknesses and layering technologies. All STERIS tabletop pads are hypoallergenic, compliant with fire code regulations and not made with natural rubber latex. STERIS pads are ultrasonically welded at the seams as opposed to stitched seams, to prevent fluid penetration.



.jpg?h=306&iar=0&w=538&hash=9EB392E0F2BDF472440EEE94B5ACAE3B)